Recent Posts
Fixture Pins, their characteristics and functionality
Posted on
When it comes to fixture pins used in CNC machine centers, assembly, and other manufacturing processes, there's a variety of types, each with different shapes, materials, and functionalities tailored to specific applications. Below is a synthesized overview of the types of fixture pins and their characteristics:
Types of Fixture Pins and Their Characteristics:
- Cotter Pins:
- Shape: Typically a wired form with a split that allows it to be inserted into a hole and bent to secure it.
- Material: Often made of metal due to the need for durability and the ability to be bent without breaking.
- Functionality: Acts as a locking mechanism to hold other pins or nuts in place, especially in machine assembly applications1.
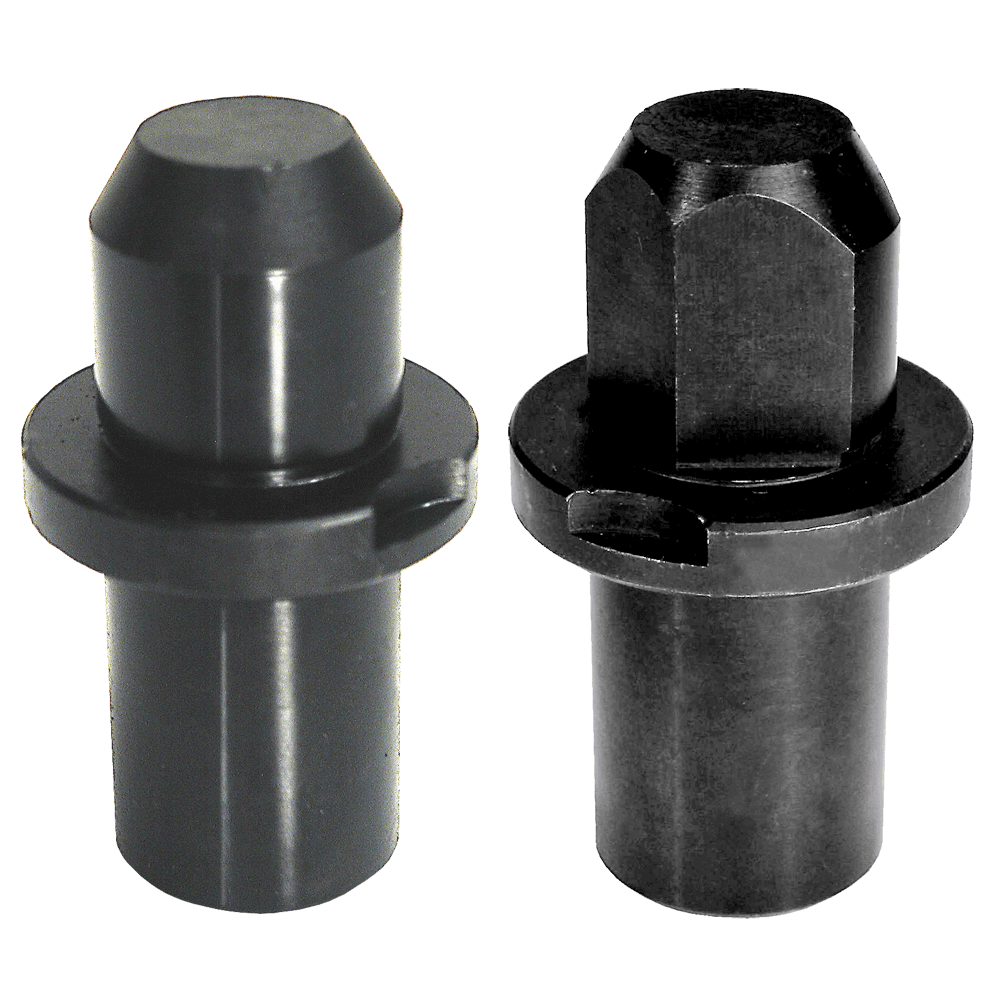
- Stepped Pins:
- Shape: These are common pins with a stepped profile, featuring either a small or large head.
- Functionality: The stepped design accommodates machining inaccuracies and ensures a smoother locating operation2.
- Diamond Shaped Pins:
- Shape: Characterized by a diamond-shaped profile.
- Functionality: The diamond shape is critical in compensating for machining inaccuracies and aids in a smoother locating operation2.
Forms of Locators in Jig & Fixture Design:
- Solid Supports:
- Shape: Fixed-height locators.
- Functionality: Precisely locate a workpiece in one axis. They may be integrated into the tool body or installed as separate components like rest buttons3.
- Adjustable Supports:
- Shape: Variable-height locators.
- Functionality: Provide adjustable support to accommodate variations in workpiece heights, commonly used for workpieces with uneven or irregular surfaces3.
- Equalizing Supports:
- Shape: A form of adjustable support.
- Functionality: Designed to float and compensate for workpiece variations; they maintain contact with the part as one side is depressed and the other raises3.
- Locating from External Edges:
- Functionality: The primary locating surface is positioned on three supports using the 3-2-1 or six-point locational method, which references and restricts the workpiece3.
- Other Locating Devices:
- Types: Include cylindrical rest buttons, flat-sided locators, vee locators, nest locators, and adjustable locators.
- Functionality: Used for locating from the external profile or internal diameter of a workpiece3.
Considerations for Fixture Pin Design:
- Material: Fixture pins are typically metal, often roll-formed, and may have minor alterations to meet individual specifications4.
- Internal Location: For locating internal diameters, the two main types are locating pins and locating plugs, with the difference being their size3.
- Design Planning: Locators must be carefully planned into the design of the workholder to ensure proper location and repeatability3.
The functionality of these pins and locators is critical for precise positioning and securing of workpieces during manufacturing, ensuring repeatability and accuracy in high-precision environments like CNC machining centers. It’s essential that these components are chosen and applied according to the specific needs of the workpiece and the machining processes involved.
 Loading... Please wait...
Loading... Please wait...
